The GIST of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors of the Stomach

Source: Shutterstock
What are Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GISTs)?
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are a rare type of soft tissue sarcoma. Sarcomas are a general term for cancers that originate from connective tissues surrounding and protecting body organs. While these tumors can occur anywhere along the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, most begin in the stomach and small intestine.
GISTs originate from specialized cells called the interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs), found in the muscle layer of the GI wall. Known as the 'pacemaker' cells of the gut, ICCs send signals that trigger muscular contractions to move food and liquids through the digestive tract. This process is called peristalsis.
Under normal conditions, these cells grow and divide to replace old or damaged cells that eventually die. However, when this process goes awry, abnormal or damaged cells can avoid cell death and continue to grow uncontrollably. This leads to the formation of a mass of cells called a tumor, which becomes malignant (cancerous) when it invades nearby tissues and has the potential of spreading (metastasizing) to other parts of the body.
Read on: Types of cancers within the stomach
Signs and symptoms
Smaller, early-stage GISTs grow slowly over time and usually do not give rise to any symptoms. As a result, doctors often find smaller tumors incidentally during tests and scans for other medical conditions. However, advanced GISTs that are larger and fast-growing can cause a wide range of symptoms, which may vary depending on the tumor's location.
The stomach is the most common location in the body where GISTs arise. Some symptoms associated with the growth of advanced stomach GISTs include abdominal pain, fatigue and bloody stools.
Related: Stomach GIST symptoms
Diagnosing stomach GISTs

Endoscopic images of submucosal GISTs in the stomach. Source: Gastrolab/Science Photo Library
Once your doctors suspect that you may have a GIST, you will undergo a series of tests and/or scans to confirm your diagnosis. This typically involves an upper endoscopy (which often includes a specialized endoscopic procedure called an endoscopic ultrasound) with biopsy. These diagnostic exams can also help to differentiate between GISTs and other cancers of the stomach.
Read on: Diagnosis of GISTs
Staging stomach GISTs
After confirming a GIST diagnosis, your doctors will need to determine the cancer’s stage. Staging is the process of describing how large a cancer has grown and how far it has spread to other parts of the body, if at all. This provides useful information about prognosis as well as guides the best treatment approach(es).
Clinical staging uses different types of exams, such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. Pathologic staging is done if and after a patient goes to surgery to remove their GIST. The pathology report will describe details, like tumor size, that comprises the final pathologic stage.
Related: Tests and scans used to stage GISTs
Find out more: Risk stratification of stomach GISTs
GIST tumor treatment
When deciding on the best treatment options for you, your doctors will take several factors into consideration. These include:
- the size of the tumor, its location within the stomach and how far it has spread
- the speed at which the tumor is growing (also known as its mitotic rate)
- if the tumor cells have certain gene mutations (changes or alterations)
This information will determine the following:
- how aggressive the GIST is
- whether the tumor can be removed with surgery and if it can be targeted by certain medications
- the risk of the GIST coming back after treatment (known as cancer recurrence)
Your treatment plan may involve different types of treatments, such as surgery, targeted therapies and liver-directed therapies.
Observation via endoscopic surveillance
Observation is the typical recommendation for GISTs smaller than 2cm, especially if they are asymptomatic and have a low risk of progression or metastasis. This approach involves regular surveillance via endoscopic techniques, like endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) with fine-needle aspiration, to assess any changes in the tumor size or behavior over time.
Surgical resection should be considered if endoscopic surveillance reveals that the GIST is:
- growing significantly, or
- has features suggesting high risk of progression, such as high mitotic rate, ulceration and irregular tumor borders
Surgery
urgery is primarily used to treat GISTs that are more than 2 cm in size and can be safely removed. This includes:
- smaller, localized tumors
- larger GISTs that have spread to other organs, such as the liver, but to a limited extent
The aim of surgery is to remove all cancerous tissue.
Related: Surgery for GISTs
Targeted therapies
Targeted therapies refer to drugs specifically designed to identify and attack tumor cells while limiting damage to healthy cells. They work by targeting proteins called tyrosine kinases found inside or on the surface of tumor cells.
Tyrosine kinases send signals that promote cellular processes such as cancer cell growth and survival, angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels to supply the tumor with nutrients and oxygen) and tumor invasion and metastasis, which encourage cancer progression altogether.
By blocking the action of tyrosine kinases, these drugs, known as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), can shrink or stop the growth and spread of GISTs. They can help patients with advanced GISTs who are not candidates for surgery, as well as before and/or after surgery for patients who are undergoing an operation for their GIST.
Read on: Targeted therapy drugs used in the treatment of GISTs
Liver-directed therapies
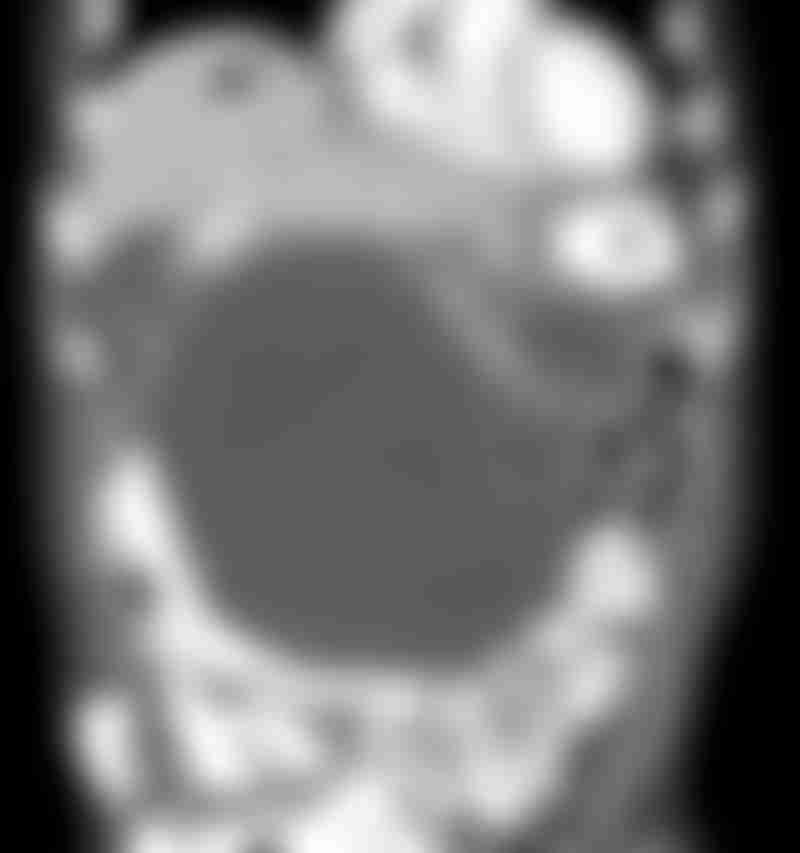
CT scan of a 80-year-old male with gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST) metastatic to the liver. There is a large 20 cm mass (arrows) arising off the stomach (asterisk) in the abdomen, with a metastatic lesion in the dome of left hepatic lobe of liver (black arrowhead). Source: Steven Needell/Science Photo Library
Ablation and embolization are two types of liver-directed treatments used for GISTs that that have spread to the liver. These treatments are utilized if surgery cannot be done to remove these tumors and often done in conjunction with targeted therapies, or if targeted therapies are not as effective as hoped.
Related: Liver-directed treatments for metastatic GISTs
Palliative radiation therapy
Radiation therapy (or radiotherapy) is the use of high-power x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from dividing. It is not commonly used to treat primary GISTs, as these tumors generally do not respond to radiotherapy. However, GISTs that have metastasized to certain sites, such as the bone, are sometimes treated with radiation therapy as part of palliative care.
Preventing stomach GISTs
There is no sure way to prevent GISTs or any other cancers of the stomach. However, there are some things you can do to lower your risk of developing stomach (or gastric) cancers in general.
Find out more: Lowering your stomach cancer risk
Life after gastric cancer
If you’ve completed active treatment and have been cleared of stomach cancer, you may be experiencing a multitude of emotions. While many may feel relieved and excited for their lives post-stomach cancer, others may find the transition to a “new normal” extremely daunting. Survivorship is different for every person who’s gone through stomach cancer.